Today, many innovative technologies exist to produce hot water for our homes, such as the solar water tank. Nevertheless, households still use traditional method of electric tanks to heat up their water for their bathroom or kitchen. Did you ever wonder how does a water tank work? We are here to present to you everything you need to know.
How does a water tank work: The stratification principle
Electric tanks work according to the stratification principle. When cold water heats up, it loses its density and goes all the way up to the top of the tank. It can then be used to cover the needs of hot water for the residents. This provides hot water quickly for the shower for example.
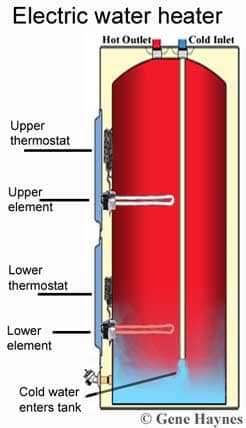
An electric tank consists of an enamel tank, a heating system, a resistance, a thermostat, and a corrosion prevention system. To bring us hot water, it uses the stratification principle which works the following way:
As the tank is emptying, pressurized cold water enters to meet your domestic hot water needs. The electric resistance inside the tank heats the cold jet which ejects it up to the reservoir. This phenomenon is possible because of the different densities of hot and cold air. On the other hand, heavier, the cold water stays at the bottom of the tank.
This physical principle spearheads the name stratification: water from different temperatures creates layers that do not mix.
Keeping the balance between hot and cold water
The pressurized cold jet could mess with the balance of hot and cold water. To solve this issue, most of the electric water tanks feature a jet breaker with an aerator that “breaks” the pressure injected from the bottom of the tank. The jet breaker preserves a natural distribution of the layers depending on their temperature.
The ideal temperature inside the tank is between 60°C and 65°C. Also, due to the isolation around the tank, the water keeps its temperature once heated up. Nevertheless, a thermostat still permanently checks the temperature, and in case of a variation, it gauges the heating system to increase it again.
The temperature will never be under 60°C as if it does, the bacteria responsible for legionella could spread, and the scaling could grow faster. On the other hand, it should not be above 65°C either to avoid any risk of scalding and the use of too much electricity

Now you know more about how does a water tank work. Nevertheless, you might still have some areas that need clarification. Do not hesitate to ask us questions in the comments section.


Im impressed by the way you embraced this subject. It really is not usually I come across a website with winning articles like yours. I will bookmark your feed to stay up to date along with your upcoming updates.Like it and do preserve up the solid work.